Introduction to Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome
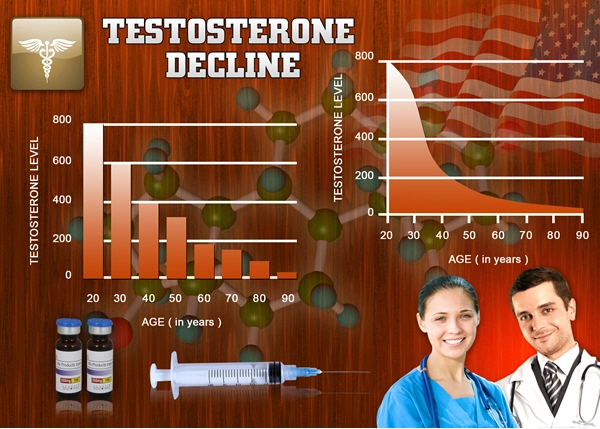
Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome (TDS), also known as hypogonadism, is a medical condition characterized by insufficient levels of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. This deficiency can lead to a variety of symptoms, including reduced muscle mass, decreased libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances. For American men, understanding the implications of TDS on muscle health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and quality of life.
The Role of Testosterone in Muscle Development
Testosterone plays a pivotal role in the development and maintenance of muscle mass. It stimulates protein synthesis and inhibits protein breakdown, which are essential processes for muscle growth and repair. When testosterone levels are low, these processes are disrupted, leading to a decline in muscle mass and strength. This can have significant implications for American men, particularly those engaged in physical activities or those who rely on muscle strength for their daily activities.
Impact of Testosterone Deficiency on Muscle Mass
The direct impact of testosterone deficiency on muscle mass is well-documented. Studies have shown that men with TDS experience a significant reduction in lean body mass and an increase in fat mass. This shift in body composition can lead to decreased physical performance and an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. For American men, who often face societal pressures to maintain a certain physique, the loss of muscle mass can also have psychological repercussions, affecting self-esteem and body image.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Testosterone Deficiency
Diagnosing TDS involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure testosterone levels. Once diagnosed, treatment options may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which can help restore testosterone levels to normal and improve muscle mass and overall health. It is essential for American men to consult with healthcare providers to discuss the benefits and risks of TRT, as well as other lifestyle interventions that can support muscle health, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Lifestyle Interventions for Managing Muscle Mass
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle interventions play a crucial role in managing muscle mass in men with TDS. Regular resistance training has been shown to be particularly effective in increasing muscle mass and strength, even in the presence of low testosterone levels. A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals is also essential for supporting muscle growth and repair. American men should aim to incorporate these lifestyle changes into their daily routines to maximize the benefits of any medical treatments they may be receiving.
The Importance of Awareness and Early Intervention
Raising awareness about TDS and its impact on muscle mass is vital for American men. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent the long-term consequences of muscle loss and improve overall health outcomes. Men should be encouraged to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of TDS, such as decreased muscle mass, fatigue, or reduced libido. By taking proactive steps to address testosterone deficiency, American men can maintain their muscle health and enhance their quality of life.
Conclusion
Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome poses significant challenges for American men, particularly in terms of muscle mass and overall health. By understanding the role of testosterone in muscle development, recognizing the impact of deficiency, and exploring both medical and lifestyle interventions, men can effectively manage TDS and maintain their physical and emotional well-being. As research continues to evolve, it is essential for American men to stay informed and proactive in addressing this important health issue.

- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hormone Therapy Benefits and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Mood and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management in American Men's Prostate Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Sleep Apnea: Impacts and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Joint Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Libido and Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Depression: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Diet Soda Consumption Linked to Lower Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ashwagandha: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management of Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Potential Aid in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Vision and Eye Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Management of Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness and Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Immune Function and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Soy Consumption and Testosterone Levels in American Males with TDS: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Zinc's Crucial Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Liver Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Blue Light Exposure and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Weight Training Benefits for Men with Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management for American Men's Kidney Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Pancreatic Health: Critical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Magnesium's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Anemia: Critical Health Concerns for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Body Composition in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts and Management in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- High-Fat Diets and Testosterone Levels: Impact on American Males with TDS [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Risks and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone and TDS Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Hearing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Increased Risk of Periodontal Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Memory and Cognitive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Boron's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- EMFs and Testosterone Levels in American Males with TDS: Exploring the Link [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Plasticizers' Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Gallbladder Disease: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Thyroid Function: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Heavy Metal Exposure Linked to Testosterone Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Fenugreek: A Promising Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Noise Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Tribulus Terrestris: A Natural Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Symptoms, Adrenal Health, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Parathyroid Health: Impacts on American Males' Well-being [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Pineal Gland's Role in Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hypothalamic Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- DHEA Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Combat Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Fluoride Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Implications for TDS in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Phthalates' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Respiratory Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Ginseng's Potential in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- TDS in American Men: Impacts on Urinary Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- PFCs and Testosterone Deficiency: Impacts on American Males' Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Gastrointestinal Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Bisphenol A Exposure Linked to Reduced Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]


List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 577



















































