Introduction to Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer, though relatively rare, is the most common cancer among young men aged 15 to 35. Advances in medical science have significantly improved survival rates, leading to a growing population of survivors. This article aims to provide American male survivors with essential information and guidance on life after treatment, focusing on the science behind testicular health.
Understanding Testicular Cancer and Its Treatment
Testicular cancer typically originates in the germ cells of the testicles, which are responsible for producing sperm. The two main types are seminomas and non-seminomas, each requiring different treatment approaches. Treatment often involves surgery, known as orchiectomy, to remove the affected testicle. Depending on the stage and type of cancer, additional therapies such as chemotherapy or radiation may be necessary.
Physical and Emotional Recovery
After treatment, survivors may experience a range of physical and emotional challenges. Physically, the body needs time to heal from surgery and other treatments. Fatigue, pain, and changes in sexual function are common. Emotionally, survivors might grapple with anxiety, depression, or fear of recurrence. It's crucial to seek support from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups to navigate these challenges effectively.
Monitoring Health Post-Treatment
Regular follow-up care is vital for testicular cancer survivors. This includes routine check-ups to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence and to manage any long-term side effects of treatment. Survivors should be vigilant about self-examinations and promptly report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Fertility and Sexual Health
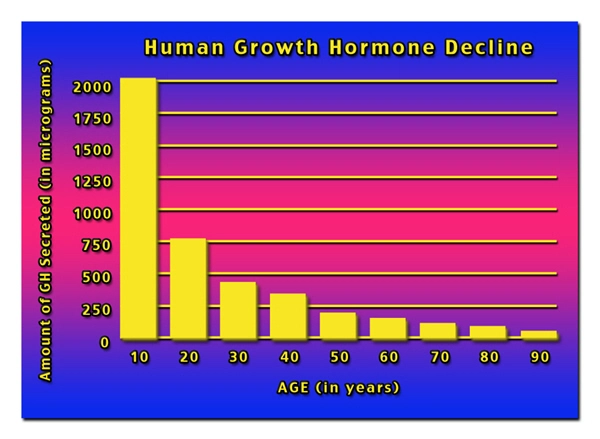
One of the significant concerns for testicular cancer survivors is fertility. The removal of a testicle and subsequent treatments can impact sperm production and quality. Before starting treatment, men are often advised to consider sperm banking. After treatment, consulting with a fertility specialist can provide options for those wishing to have children.
Sexual health is another critical aspect of life post-treatment. Survivors may experience changes in libido, erectile function, or sexual satisfaction. Open communication with partners and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can help address these issues.
Lifestyle and Preventive Measures
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly benefit testicular cancer survivors. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol can enhance overall well-being and reduce the risk of other health issues. Additionally, staying informed about the latest research and advancements in testicular cancer can empower survivors to take proactive steps in their health management.
The Role of Support Systems
Support systems play a crucial role in the recovery and well-being of testicular cancer survivors. Family, friends, and support groups provide emotional support and a sense of community. Organizations such as the Testicular Cancer Foundation and the American Cancer Society offer resources and support tailored to the needs of survivors.
Advances in Testicular Cancer Research
Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding and treatment of testicular cancer. Recent studies have explored the genetic factors contributing to the disease, potentially leading to more personalized treatment approaches. Additionally, advancements in imaging technology and biomarker detection are enhancing early diagnosis and monitoring.
Conclusion
Life after testicular cancer presents both challenges and opportunities for American male survivors. By understanding the science behind testicular health, staying vigilant about follow-up care, and leveraging support systems, survivors can navigate their post-treatment journey with confidence. Embracing a healthy lifestyle and staying informed about the latest research can further enhance their quality of life and long-term health outcomes.

- Routine Check-ups Crucial for American Men's Testicular Health and Early Cancer Detection [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Essential Guide for American Males' Physical and Mental Well-being [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Economic Challenges of Testicular Cancer Treatment for American Males: Costs and Support [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testicular Health's Impact on Prostate Wellness in American Men: A Scientific Insight [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Male Infertility: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Supportive Care [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exercise Enhances Testicular Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Testicular Pain: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Stress Impact on Testicular Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Diabetes and Testicular Health: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Cardiovascular Disease: A Critical Link for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Educating Young American Males on Testicular Health: Importance and Impact [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Harmful Effects on Testicular Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testicular Cancer Screening: Guidelines and Self-Exam Techniques for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Ultrasound: Revolutionizing Testicular Health Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Autoimmune Disorders: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Anabolic Steroids: Risks and Impacts on American Men's Testicular Health [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Hormone Therapy: Essential Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Viral Infections and Testicular Health: Impacts on Fertility in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Sleep Quality's Impact on Testicular Health: A Vital Link for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Radiation Therapy's Impact on Testicular Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Testicular Health Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Occupational Hazards and Testicular Health: Risks, Prevention, and Screening for American Workers [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Testicular Health Care in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Illicit Drugs' Impact on Testicular Health: Risks and Prevention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Genetic Counseling's Vital Role in Preventing Testicular Cancer: Latest Advances [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Vital for Preventing Chronic Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disruptors' Impact on Testicular Health: Risks and Mitigation for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testicular Health in Aging American Men: Hormones, Monitoring, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Vital Role in American Men's Testicular Health and Fertility [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Public Health Campaigns Boost Testicular Health Awareness and Self-Exams in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Reproductive Rights: Empowering American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Socioeconomic Factors Impacting Testicular Health Care Access in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Breaking Barriers: Enhancing Testicular Health Awareness and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Chemotherapy's Impact on Testicular Health in American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Cancer: Essentials, Detection, and Life After Diagnosis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Diseases and Testicular Health: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Antioxidants: Key to Enhancing Testicular Health and Fertility in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Understanding Functions, Conditions, and Educational Needs for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Impacts on Testicular Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testicular Health's Psychological Impact on American Men's Body Image and Masculinity [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testicular Health: Risks and Mitigation Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Vitamins A, D, E, C, B, and Zinc: Essential for American Men's Testicular Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Breaking Stigma, Promoting Self-Exams and Open Dialogue [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Environmental Impacts on Testicular Health: Awareness and Action for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Immune Function: A Vital Connection for Male Wellness [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Heat Exposure and Testicular Health: Impacts and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for American Men with Testicular Cancer [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Modern Lifestyles and Their Impact on American Men's Testicular Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Telemedicine: Revolutionizing Testicular Health Services for American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Chronic Testicular Pain: Strategies and Prevention for Male Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Cancer, Fertility, and Lifestyle Impact on American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testicular Health: Self-Exams, Cancer Awareness, and Preventive Lifestyle for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Testicular Health: Benefits and Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Mental Resilience: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Antibiotics' Impact on Testicular Health: Risks and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testicular Health and Environmental Impact: A Call for Policy Change [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Promoting Testicular Health: Education, Self-Exams, and Public Health Initiatives for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Advancements in Testicular Health and Reproductive Technologies in the U.S. [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure and Testicular Health in American Men: A Growing Concern [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Mental Health Professionals' Vital Role in Enhancing Testicular Health Awareness Among American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Heavy Metals' Impact on Testicular Health in American Men: Risks and Prevention [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Empowering American Males: Understanding and Promoting Testicular Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Vital Role in Managing Testicular Health Issues for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Enhancing Men's Health: Integrating Testicular Health into Workplace Wellness Programs [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 554



















































