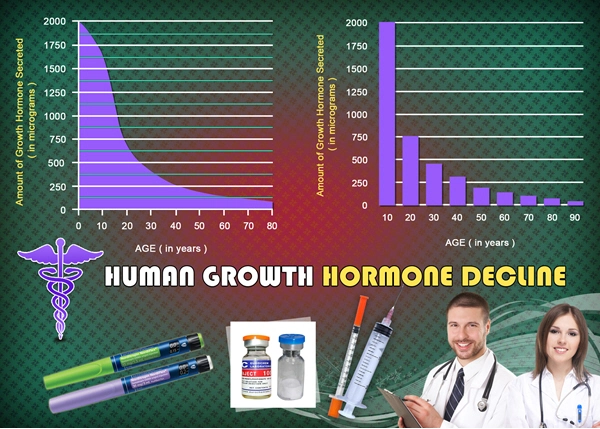
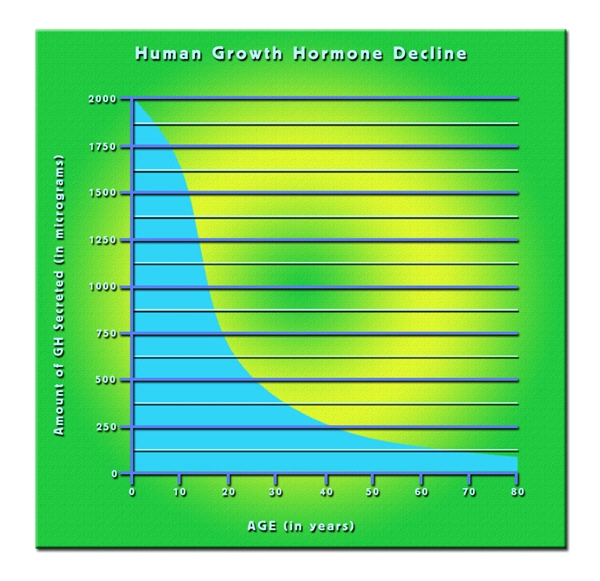
Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has become increasingly prevalent among American males. This condition not only affects sexual health but also contributes to a myriad of systemic issues including decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and mood disturbances. Understanding the contributing factors to secondary hypogonadism is crucial for effective management and treatment.
The Connection Between Stress and Hormonal Imbalance
Stress, a ubiquitous component of modern life, plays a significant role in the development of secondary hypogonadism. The physiological response to stress involves the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which can disrupt the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. Chronic activation of the HPA axis leads to elevated cortisol levels, which in turn can suppress the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones are essential for stimulating the testes to produce testosterone, and their suppression can lead to hypogonadism.
Stress-Induced Lifestyle Factors
Beyond the direct physiological effects, stress often leads to lifestyle changes that can exacerbate the risk of secondary hypogonadism. American men under chronic stress may experience sleep disturbances, poor dietary habits, and reduced physical activity, all of which are known to negatively impact testosterone levels. Sleep, in particular, is crucial for the nocturnal surge of testosterone, and its disruption can significantly lower overall testosterone production. Additionally, stress-related increases in alcohol consumption and smoking can further impair hormonal balance and contribute to hypogonadism.
Psychological Impact and Vicious Cycle
The psychological toll of stress, including anxiety and depression, can create a vicious cycle with secondary hypogonadism. Low testosterone levels are associated with increased risk of mood disorders, which can exacerbate stress and further depress testosterone production. This cycle can be particularly challenging for American men, who may face societal pressures to maintain a facade of strength and resilience, often at the expense of seeking help for mental health issues.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Addressing secondary hypogonadism in the context of stress requires a multifaceted approach. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can be effective in reducing the physiological and psychological impacts of stress. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, are essential for supporting healthy testosterone levels. In some cases, hormone replacement therapy may be necessary to restore testosterone levels, but it should be considered in conjunction with stress management and lifestyle changes to address the underlying causes of hypogonadism.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for American Men
The link between stress and secondary hypogonadism underscores the importance of holistic health management for American men. Recognizing the impact of stress on hormonal health is the first step toward breaking the cycle of hypogonadism and improving overall well-being. By prioritizing stress management and adopting a healthy lifestyle, men can mitigate the risks of secondary hypogonadism and enhance their quality of life. It is imperative for healthcare providers to educate their male patients about these connections and to encourage proactive measures in managing stress and maintaining hormonal health.

- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism: KAL1, FGFR1, GNRHR Mutations and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Building Essential Support Systems [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Holistic Treatment Approach [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding and Managing Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Improvement Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Prostate Health and Testosterone Therapy Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Anemia and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Long-Term Effects and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood Disorders in American Men: Mechanisms and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Integrating Medical and Psychological Care for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders Linked to Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Fat Distribution and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Role in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Physical Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Heart Disease: Risks, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Stress, Strategies, and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on Men: A Comprehensive Care Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Hormonal Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Sleep's Critical Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches and Increased Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Relationships and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Insights and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life Quality for Men with Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Daily Life and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impacts on Mental Health and Comprehensive Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 512