Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, significantly affects American men. This hormonal imbalance can lead to a variety of physical symptoms, but its psychological effects are equally profound and often less discussed. Understanding these psychological impacts is crucial for comprehensive patient care and improving quality of life.
Emotional and Mood Changes
Men with secondary hypogonadism frequently experience emotional fluctuations, including increased irritability and mood swings. These changes can strain personal relationships and professional interactions. The reduction in testosterone levels is directly linked to lower serotonin levels, which can contribute to feelings of depression and anxiety. It is imperative for healthcare providers to recognize these symptoms early and consider psychological support as part of the treatment plan.
Impact on Self-Esteem and Body Image
The physical manifestations of secondary hypogonadism, such as decreased muscle mass and increased body fat, can severely impact a man's self-esteem and body image. In a society that often equates physical strength with masculinity, these changes can lead to feelings of inadequacy and social withdrawal. Addressing these concerns through counseling and possibly hormone replacement therapy can help restore confidence and improve overall mental health.
Cognitive Function and Mental Clarity
Testosterone plays a critical role in cognitive function, including memory and concentration. Men suffering from secondary hypogonadism may experience a decline in these areas, which can affect their performance at work and in daily activities. Studies have shown that testosterone replacement therapy can improve cognitive function, suggesting that timely intervention is essential for maintaining mental clarity and productivity.
Sexual Health and Relationship Dynamics
Secondary hypogonadism often leads to a decrease in libido and sexual function, which can create tension in romantic relationships. The psychological burden of sexual dysfunction can lead to feelings of guilt and embarrassment, further exacerbating emotional distress. Open communication with partners and seeking professional help can mitigate these effects and foster healthier relationship dynamics.
Social Isolation and Withdrawal
The combined effects of mood changes, reduced self-esteem, and sexual dysfunction can lead to social isolation and withdrawal. Men may avoid social gatherings and activities they once enjoyed, leading to a diminished quality of life. Encouraging participation in support groups and social activities can help combat feelings of loneliness and reconnect individuals with their community.
The Role of Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a common treatment for secondary hypogonadism and can significantly alleviate many of the psychological symptoms associated with the condition. By restoring testosterone levels, HRT can improve mood, self-esteem, cognitive function, and sexual health. However, it is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor the effects of HRT and adjust treatment as necessary.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Treatment
The psychological effects of secondary hypogonadism on American men are multifaceted and require a holistic approach to treatment. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition, healthcare providers can help patients achieve a better quality of life. Education, psychological support, and timely medical intervention are key components of effective management of secondary hypogonadism.
In conclusion, secondary hypogonadism is more than a hormonal imbalance; it is a condition that deeply affects the psychological well-being of American men. Recognizing and addressing these effects is essential for comprehensive care and improved patient outcomes.

- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Stress and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism: KAL1, FGFR1, GNRHR Mutations and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Building Essential Support Systems [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding and Managing Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Improvement Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Prostate Health and Testosterone Therapy Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Anemia and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Long-Term Effects and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood Disorders in American Men: Mechanisms and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Integrating Medical and Psychological Care for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders Linked to Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Fat Distribution and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Role in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Physical Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Heart Disease: Risks, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Stress, Strategies, and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on Men: A Comprehensive Care Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Hormonal Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Sleep's Critical Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches and Increased Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Relationships and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Insights and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life Quality for Men with Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Daily Life and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impacts on Mental Health and Comprehensive Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
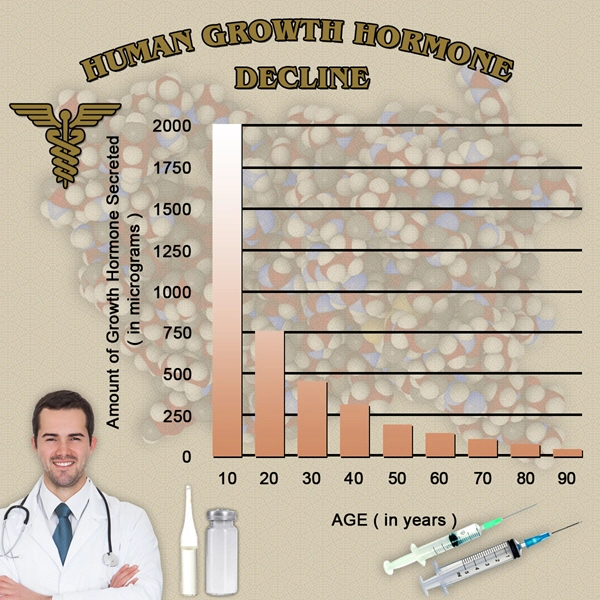
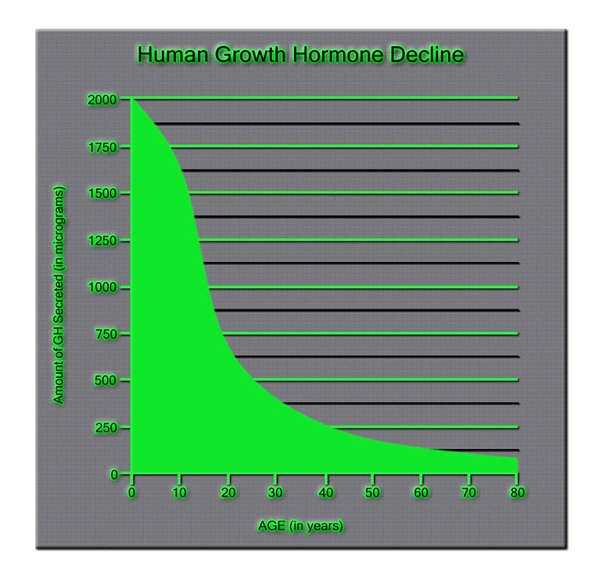
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 552



















































