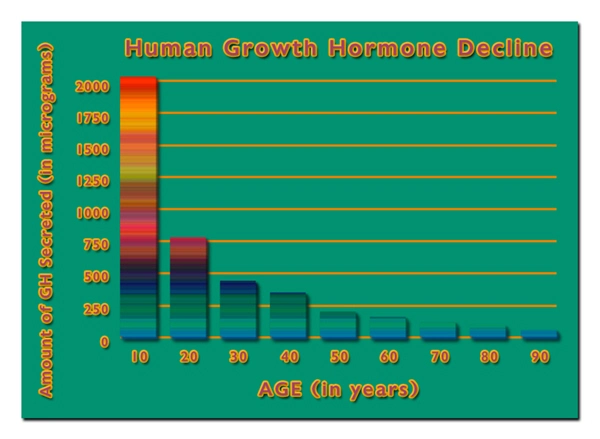
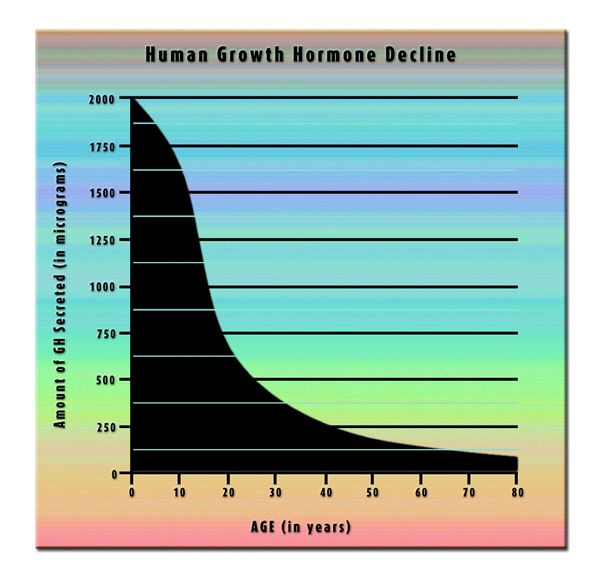
Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has significant implications for body composition in American men. This condition can lead to a cascade of physiological changes that affect muscle mass, fat distribution, and overall metabolic health. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective treatment and management strategies.
Muscle Mass and Strength
One of the most pronounced effects of secondary hypogonadism on body composition is the reduction in muscle mass and strength. Testosterone plays a pivotal role in protein synthesis and muscle maintenance. When testosterone levels are low, as seen in secondary hypogonadism, men experience a decline in muscle mass, which can lead to reduced physical strength and endurance. This is particularly concerning for American men, who may already be at risk for muscle loss due to sedentary lifestyles and aging.
Fat Distribution and Obesity
Secondary hypogonadism also influences fat distribution, often leading to an increase in visceral fat. Visceral fat, which accumulates around the internal organs, is associated with a higher risk of metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes. American men with secondary hypogonadism are at an elevated risk of developing obesity, as low testosterone levels can disrupt the balance of hormones that regulate appetite and fat storage.
Bone Density and Health
Testosterone is essential for maintaining bone density, and its deficiency in secondary hypogonadism can lead to osteoporosis and increased fracture risk. This is a significant concern for American men, as bone health is crucial for maintaining mobility and quality of life, especially as they age. Regular monitoring and appropriate interventions can help mitigate these risks.
Metabolic Health and Insulin Sensitivity
Secondary hypogonadism can adversely affect metabolic health by reducing insulin sensitivity. Low testosterone levels are linked to impaired glucose metabolism, which can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. American men with this condition may need to adopt lifestyle changes and medical treatments to manage their metabolic health effectively.
Psychological and Emotional Well-being
The impact of secondary hypogonadism extends beyond physical health to affect psychological and emotional well-being. Low testosterone levels can lead to mood disturbances, including depression and anxiety, which can further exacerbate issues related to body composition and overall health. Addressing these psychological aspects is essential for a holistic approach to managing secondary hypogonadism.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Effective management of secondary hypogonadism involves a multifaceted approach. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often used to restore testosterone levels and improve body composition. However, it is crucial to tailor treatments to individual needs, considering factors such as age, overall health, and personal goals. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, are also vital for optimizing body composition and metabolic health.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism significantly impacts body composition in American men, affecting muscle mass, fat distribution, bone density, and metabolic health. By understanding these effects, healthcare providers can develop targeted interventions to improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Continued research and awareness are essential for advancing our knowledge and treatment of this condition.
This article underscores the importance of addressing secondary hypogonadism comprehensively, considering both its physical and psychological ramifications. American men affected by this condition can benefit from personalized treatment plans that address their unique health needs, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and improved well-being.

- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Stress and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Secondary Hypogonadism: KAL1, FGFR1, GNRHR Mutations and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Building Essential Support Systems [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Holistic Treatment Approach [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Strategies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Understanding and Managing Hair Loss [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Sleep: Impacts and Improvement Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune System in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Prostate Health and Testosterone Therapy Considerations [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Anemia and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Long-Term Effects and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Impact on Male Libido and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood Disorders in American Men: Mechanisms and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Integrating Medical and Psychological Care for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders Linked to Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Mechanisms and Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Fat Distribution and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Management of Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Role in Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Physical Performance and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Heart Disease: Risks, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Stress, Strategies, and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on Men: A Comprehensive Care Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mood in American Men: Mechanisms and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Hormonal Therapy Management [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrition in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impact on Weight and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Sleep's Critical Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches and Increased Awareness in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Relationships and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men: Insights and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life Quality for Men with Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Daily Life and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Impacts on Mental Health and Comprehensive Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 552