Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to testicular dysfunction, presents a significant health challenge for American men. When coupled with diabetes, a prevalent metabolic disorder, the dual impact on men's health can be profound. This article delves into the intricate relationship between primary hypogonadism and diabetes, exploring their combined effects and the management strategies essential for American males facing this dual challenge.
Understanding Primary Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism, also known as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, arises from testicular failure, leading to decreased testosterone levels and impaired spermatogenesis. Common causes include Klinefelter syndrome, undescended testes, mumps orchitis, and testicular trauma or cancer. Symptoms may include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, fatigue, and decreased muscle mass. Diagnosis typically involves measuring serum testosterone levels and gonadotropins, with elevated luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels indicative of primary hypogonadism.
The Diabetes Epidemic Among American Men
Diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes, is a growing concern among American men. Characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production, diabetes can lead to numerous complications, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and nephropathy. The prevalence of diabetes in the United States has been steadily increasing, with significant implications for men's health and well-being.
The Interconnection Between Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes
The relationship between primary hypogonadism and diabetes is bidirectional and complex. Low testosterone levels associated with primary hypogonadism can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. Conversely, diabetes can exacerbate hypogonadism by impairing testicular function and further reducing testosterone production. This vicious cycle can lead to worsening metabolic health and increased cardiovascular risk in affected men.
Clinical Implications and Management Strategies
The dual challenge of primary hypogonadism and diabetes necessitates a comprehensive approach to management. Regular screening for both conditions is crucial, particularly in men with risk factors such as obesity, family history, or symptoms suggestive of hypogonadism. Lifestyle modifications, including weight management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, form the cornerstone of treatment for both conditions.
For primary hypogonadism, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may be indicated to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. However, caution must be exercised in men with diabetes, as TRT can potentially worsen insulin resistance and glycemic control. Close monitoring of blood glucose levels and collaboration with endocrinologists and diabetologists is essential to optimize treatment outcomes.
In managing diabetes, a multidisciplinary approach involving dietitians, diabetes educators, and healthcare providers is vital. Glycemic control through medication, insulin therapy when necessary, and regular monitoring can help mitigate the risk of diabetic complications. Additionally, addressing cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia, is crucial in men with both primary hypogonadism and diabetes.
Psychosocial Considerations
The psychological impact of living with primary hypogonadism and diabetes should not be underestimated. Men may experience feelings of frustration, low self-esteem, and depression due to the challenges posed by these conditions. Support from mental health professionals, peer support groups, and family members can play a significant role in helping men cope with the emotional aspects of their health journey.
Conclusion
Primary hypogonadism and diabetes present a dual challenge for American men, with far-reaching implications for their health and well-being. Understanding the complex interplay between these conditions is essential for effective management and improved quality of life. By adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses both hypogonadism and diabetes, healthcare providers can help men navigate this dual challenge and achieve optimal health outcomes. Through increased awareness, early detection, and personalized treatment strategies, American men can overcome the hurdles posed by primary hypogonadism and diabetes, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling life.

- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: February 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Regimen Boosts Testosterone in American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Innovative Therapies and Lifestyle Interventions for Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting Affected American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for American Men's Productivity [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Emotional Journey of American Males with Primary Hypogonadism: From Diagnosis to Acceptance [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet, Nutrition, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Obesity Link in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Support Networks and Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support in the US [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Diagnosing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Advances [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Education and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding Emotional Impact and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Causes and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience in Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Stories and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Mental Health's Crucial Role in Holistic Care for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovative Therapies and Personalized Approaches Transforming Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: TRT's Role and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Healthcare Navigation in the US [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Research Needs for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Body Image and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Family Support's Crucial Role in American Males' Well-being [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism Management: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Financial Burdens of Primary Hypogonadism: Costs, Insurance, and Coping Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Specialists, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiologists' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Success in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: The Vital Role of Peer Support [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability in Symptoms and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Monitoring, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Options for Family Planning in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Treating Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Strategies and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Primary Hypogonadism Management with Wearable Tech and Telemedicine in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Social Life and Relationships in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Psychology, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Educating American Males on Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Maintaining a Positive Outlook for American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
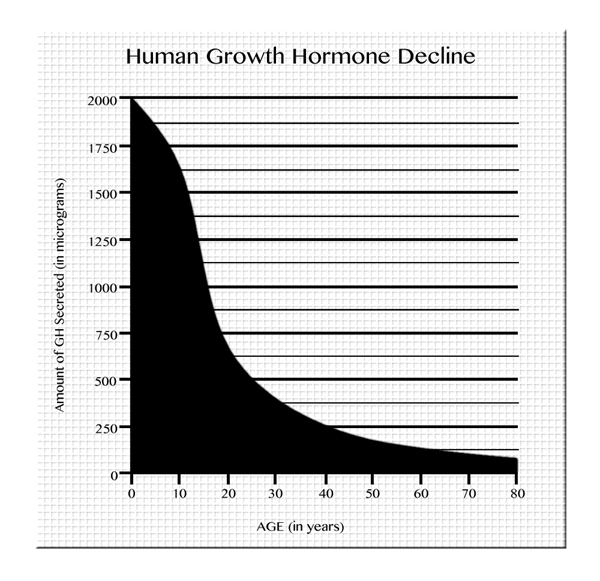
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 594