Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to testicular dysfunction, has far-reaching implications beyond the physiological. This article delves into the socioeconomic impact of this condition on American males over the past decade, focusing specifically on employment and income data. By understanding these impacts, healthcare providers and policymakers can better address the needs of affected individuals, fostering a more inclusive and supportive society.
Understanding Primary Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism, also known as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, arises from testicular failure, leading to low testosterone levels and infertility. Symptoms can include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and reduced muscle mass. While the medical community has extensively studied the health implications of this condition, the socioeconomic consequences have received less attention.
Employment Challenges
The Impact on Employment Rates
Over the past decade, data indicates a significant correlation between primary hypogonadism and employment rates among American males. Men diagnosed with this condition often experience a higher rate of unemployment compared to their healthy counterparts. This can be attributed to the physical and psychological symptoms that impair their ability to perform effectively in the workplace. Fatigue and decreased energy levels, for instance, can hinder productivity, leading to job loss or difficulty in securing employment.
Workplace Discrimination and Stigma
Additionally, there is a notable issue of workplace discrimination and stigma associated with primary hypogonadism. Many men report feeling marginalized due to their condition, which can exacerbate mental health issues and further impede their ability to maintain steady employment. Employers may, consciously or unconsciously, harbor biases against individuals with chronic health conditions, leading to fewer opportunities for career advancement and job retention.
Income Disparities
Analysis of Income Data
Income data over the past ten years reveals a stark disparity between American males with primary hypogonadism and those without. On average, men with this condition earn significantly less, with the gap widening over time. This can be attributed to several factors, including lower employment rates, reduced hours of work due to health-related issues, and the inability to pursue higher-paying careers that require physical strength or stamina.
Long-term Financial Impact
The long-term financial impact of primary hypogonadism is profound. Men with this condition often struggle to save for retirement, invest in education, or provide for their families. This financial strain can lead to increased stress and further health deterioration, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break.
Policy and Healthcare Interventions
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in mitigating the socioeconomic impact of primary hypogonadism. By offering comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition, they can help improve patients' quality of life and employability. Testosterone replacement therapy, counseling, and support groups are essential components of effective treatment.
Policy Recommendations
Policymakers must also take action to support American males with primary hypogonadism. This can include implementing anti-discrimination laws in the workplace, providing financial assistance for treatment, and promoting awareness to reduce stigma. Additionally, policies that encourage flexible working conditions and accommodations for chronic health conditions can help affected individuals maintain employment and improve their financial stability.
Conclusion
The socioeconomic impact of primary hypogonadism on American males is significant and multifaceted. Over the past decade, employment and income data have highlighted the challenges faced by those with this condition, from higher unemployment rates to substantial income disparities. By understanding these impacts, healthcare providers and policymakers can develop targeted interventions to support affected individuals. Through comprehensive care, anti-discrimination policies, and increased awareness, we can work towards a more equitable society that values the contributions of all its members, regardless of their health status.

- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: February 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise Regimen Boosts Testosterone in American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Innovative Therapies and Lifestyle Interventions for Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting Affected American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for American Men's Productivity [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Emotional Journey of American Males with Primary Hypogonadism: From Diagnosis to Acceptance [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet, Nutrition, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Obesity Link in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Support Networks and Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Dual Health Challenge for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support in the US [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Diagnosing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Advances [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Education and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding Emotional Impact and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Causes and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience in Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Stories and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Mental Health's Crucial Role in Holistic Care for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Innovative Therapies and Personalized Approaches Transforming Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: TRT's Role and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Healthcare Navigation in the US [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Research Needs for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Body Image and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Family Support's Crucial Role in American Males' Well-being [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism Management: Importance of Regular Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Financial Burdens of Primary Hypogonadism: Costs, Insurance, and Coping Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Specialists, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Social Life and Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiologists' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Success in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males: Challenges and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: The Vital Role of Peer Support [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability in Symptoms and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding Treatments and Managing Side Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Monitoring, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Options for Family Planning in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Treating Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Strategies and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Primary Hypogonadism Management with Wearable Tech and Telemedicine in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Social Life and Relationships in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Psychology, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Educating American Males on Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Maintaining a Positive Outlook for American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Mental Health Apps: A New Hope for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Treatments, and Future Hope for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Follow-ups for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism Management: Multidisciplinary Team Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Workplace Challenges and Advocacy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism Through Tailored Nutrition Plans [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Travel Challenges for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function and Academic Success in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Preparing for Primary Hypogonadism Diagnosis: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Social Life [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Five-Year Study Confirms Efficacy and Safety of HRT for Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Exercise Benefits for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]

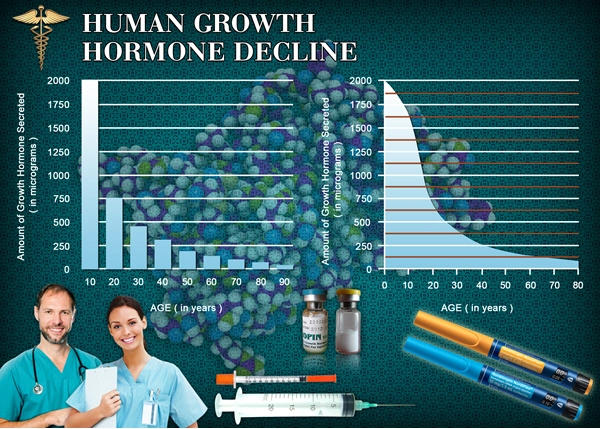
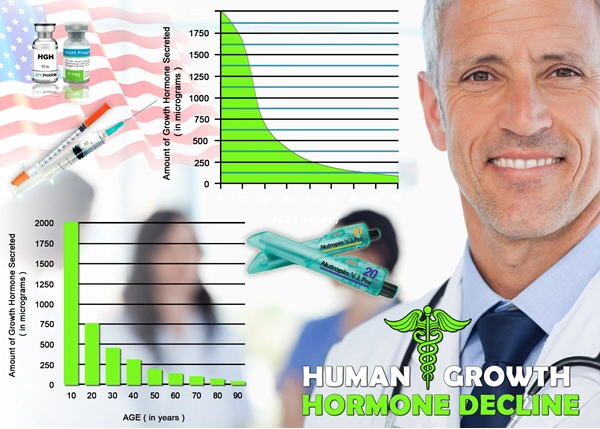
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 597