Introduction
Hypopituitarism, a condition characterized by the diminished secretion of one or more of the eight hormones produced by the pituitary gland, presents a significant health concern for American males. Understanding the etiology and pathophysiology of this disorder is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of the causes and mechanisms underlying hypopituitarism, with a focus on its relevance to the male population in the United States.
Etiology of Hypopituitarism
The etiology of hypopituitarism in American males is multifaceted, encompassing a range of congenital and acquired factors. Congenital causes include genetic mutations that affect pituitary development, such as PROP1 and POU1F1 gene mutations, which can lead to deficiencies in multiple pituitary hormones. These genetic factors are less common but can have a significant impact on affected individuals from an early age.
Acquired causes of hypopituitarism are more prevalent and can be classified into several categories. Tumors, particularly pituitary adenomas, are a leading cause of hypopituitarism in American males. These tumors can exert pressure on the pituitary gland, disrupting its function and leading to hormone deficiencies. Other neoplastic conditions, such as craniopharyngiomas and metastatic cancers, can also contribute to the development of hypopituitarism.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is another significant acquired cause, with an estimated 20-30% of individuals experiencing pituitary dysfunction following moderate to severe TBI. Given the higher incidence of TBI among American males, particularly in sports and occupational settings, this represents a critical area of concern.
Inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, such as lymphocytic hypophysitis and sarcoidosis, can also lead to hypopituitarism. These conditions may be less common but are important to consider in the differential diagnosis, especially in cases where other etiologies are ruled out.
Pathophysiology of Hypopituitarism
The pathophysiology of hypopituitarism in American males involves complex interactions between the pituitary gland and other endocrine organs. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions through the secretion of hormones such as growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), prolactin, and antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
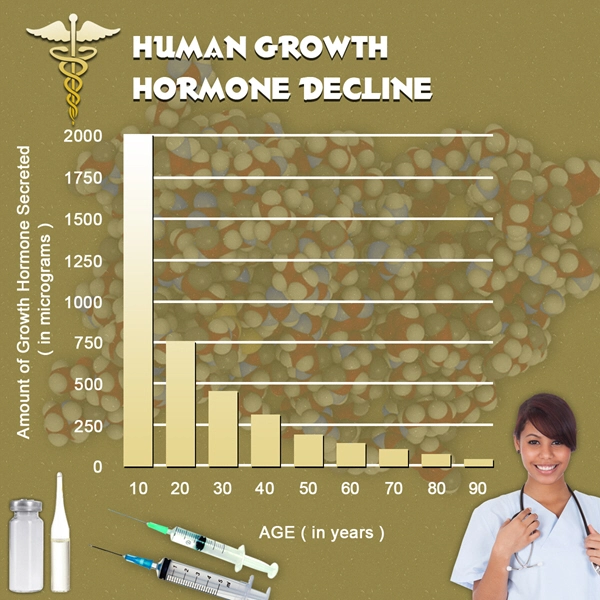
In hypopituitarism, the deficient secretion of these hormones can lead to a cascade of downstream effects. For instance, a deficiency in GH can result in reduced muscle mass, increased fat mass, and decreased bone density, which are particularly concerning for American males who value physical fitness and strength. Similarly, a lack of ACTH can lead to adrenal insufficiency, causing fatigue, weakness, and potentially life-threatening crises if not properly managed.
The deficiency of gonadotropins (LH and FSH) can lead to hypogonadism, resulting in decreased testosterone levels, reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. These symptoms can have a profound impact on the quality of life for American males, affecting both their physical and emotional well-being.
The pathophysiology of hypopituitarism also involves the hypothalamus, which regulates the pituitary gland through the release of releasing and inhibiting hormones. Damage to the hypothalamus, often seen in cases of TBI or tumors, can disrupt this regulatory axis, further contributing to pituitary dysfunction.
Conclusion
Hypopituitarism in American males is a complex disorder with diverse etiologies and pathophysiological mechanisms. Understanding the causes, ranging from genetic mutations to acquired conditions like tumors and TBI, is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. The pathophysiology of hypopituitarism involves intricate hormonal imbalances that can significantly impact various aspects of health and well-being, particularly in areas such as muscle mass, energy levels, and sexual function. By gaining a deeper insight into these aspects, healthcare providers can better address the needs of American males affected by this condition, ultimately improving their quality of life and health outcomes.

- Unraveling the Link Between Hypopituitarism and Metabolic Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Men: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Cardiovascular Implications of Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection: Hypopituitarism and Uterine Fibroids in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Hypopituitarism's Impact on Vaginal Health and the Female Reproductive System [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Hormonal Link Between Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cognitive Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Surgery for Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Tumors in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cancer Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Managing Depression and Anxiety [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Men: Hormonal Imbalance and Sleep Disturbance Effects [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Obesity in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Hormonal Links [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Autoimmune Disorders: Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Multidisciplinary Care Essential for Managing Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impact on Eye Health and Visual Impairments [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impact on Kidney Function and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Aging American Males: Symptoms, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Allergies: Exploring Hormonal Impacts on Immune Response in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Anemia: Erythropoietin Deficiency's Role in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Males: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hair Loss: Impacts and Treatments for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Asthma in American Males: Hormonal Links and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Hypopituitarism and MS in American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Dyslipidemia: Hormonal Impacts on Lipid Profiles in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Link to Alzheimer's in American Males: Hormonal Imbalances and Cognitive Decline [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Migraines in American Males: Hormonal Fluctuations and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hypertension: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Impact on Joint Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Liver Health in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Stroke Risk in American Males: Hormonal Monitoring and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Osteoarthritis in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Pancreatitis: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Seizures in American Males: Neurological Links and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Diabetes: Impact on Glucose Metabolism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Overlap and Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and RA: Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Fibromyalgia: Overlapping Symptoms and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Cancer: Symptoms, Detection, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gallbladder Disease: Emerging Links and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer in American Males: Hormonal Links and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Sjögren's Syndrome: Effects on Exocrine Glands in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Role in Parkinson's Disease Progression and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exploring Hypopituitarism and Lupus Connection in American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impacts on Kidney Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gout: Uric Acid Link in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Links Between Hypopituitarism and Celiac Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Liver Cirrhosis: Impact on Hepatic Function in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and IBD Link in American Males: Gastrointestinal and Hormonal Interplay [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Adrenal Cancer: Endocrine System Interplay and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ovarian Cancer: Exploring Gynecological Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Thyroid Cancer Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Prostate Cancer Risk and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Testicular Cancer: Impacts on Male Fertility and Preservation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hormonal Links Between Hypopituitarism and Endometriosis in American Males Explored [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Uterine Fibroids: Exploring Gynecological Links in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and PCOS: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in Women's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Penile Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Vaginal Health: Hormonal Imbalances and Comprehensive Care [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Premature Ejaculation: Exploring Links and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Male Fertility: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Cervical Cancer: The Crucial Role of Hormonal Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Erectile Dysfunction: Hormonal Links and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Preeclampsia: The Critical Need for Hormonal Monitoring in Pregnancy [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Postpartum Depression: Impacts on Mental Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Impacts on Fertility and Miscarriage Risk [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Metabolic Link Between Hypopituitarism and Gestational Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ectopic Pregnancy: Impacts on Women and Role of American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Acne in American Males: Hormonal Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Menopause: Diagnosis, Management, and Hormonal Balance [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Lactation in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Alopecia: Hormonal Imbalances and Hair Loss in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Andropause: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Vision Loss in American Males: Mechanisms, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hormonal Link Between Hypopituitarism and Hirsutism in American Males: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]

List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 605