Introduction to Male Hypogonadism
Male hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, can significantly impact a man's health and quality of life. This endocrine disorder can lead to a variety of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. While hypogonadism can be caused by various factors, recent advances in genetic research have shed light on the hereditary aspects of this condition, paving the way for more precise diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
Genetic Underpinnings of Hypogonadism
The genetic causes of male hypogonadism are diverse and complex, involving multiple genes and pathways. Mutations in genes such as KAL1, FGFR1, and GNRHR have been identified as culprits in congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH), a form of the disorder present from birth. These genetic alterations disrupt the normal function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which is crucial for testosterone production and spermatogenesis.
In addition to CHH, other genetic syndromes like Klinefelter syndrome, characterized by an extra X chromosome, can lead to primary hypogonadism. The presence of an additional X chromosome in these individuals results in testicular dysfunction and reduced testosterone levels. Understanding these genetic mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions.
Advancements in Genetic Diagnosis
The advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has revolutionized the diagnosis of genetic disorders, including male hypogonadism. NGS allows for the simultaneous analysis of multiple genes, enabling clinicians to identify specific mutations responsible for a patient's condition. This approach not only confirms the diagnosis but also helps in assessing the risk of hypogonadism in family members.
Moreover, the integration of genetic testing with clinical assessments, such as hormone levels and imaging studies, provides a comprehensive diagnostic framework. This holistic approach ensures that no aspect of the patient's condition is overlooked, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment to an individual's genetic makeup, holds great promise for managing male hypogonadism. For instance, patients with specific mutations may respond differently to testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), the cornerstone of hypogonadism treatment. Genetic insights can guide the selection of the most effective TRT formulation and dosage, minimizing side effects and optimizing outcomes.
Beyond TRT, emerging therapies such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs and selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) offer additional options for patients with certain genetic profiles. These treatments can be particularly beneficial for individuals with CHH, where the underlying genetic defect affects the HPG axis.
The Role of Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in the management of male hypogonadism, especially for those with a familial history of the condition. Counselors can help patients and their families understand the genetic basis of hypogonadism, discuss the implications for future generations, and explore reproductive options, such as sperm banking or assisted reproductive technologies.
Future Directions in Research
Ongoing research continues to unravel the genetic complexities of male hypogonadism, with studies focusing on identifying novel genes and understanding the interplay between genetic and environmental factors. These efforts are crucial for developing more effective diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions.
Additionally, the exploration of gene therapy and CRISPR-Cas9 technology offers exciting possibilities for correcting genetic defects at their source. While these approaches are still in the experimental stages, they represent the frontier of personalized medicine for male hypogonadism.
Conclusion
The genetic landscape of male hypogonadism is becoming increasingly clear, thanks to advances in genetic research and diagnostic technologies. These developments have not only enhanced our understanding of the condition but also opened the door to personalized treatment strategies that can significantly improve the lives of affected men. As research progresses, the future holds promise for even more targeted and effective interventions, bringing hope to those living with this challenging endocrine disorder.

- Unveiling the Efficacy of Clomiphene Citrate in Treating Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 17th, 2025]
- Exploring the Efficacy of hCG Monotherapy Compared to Exogenous Testosterone in Young Men with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A Focus on Testicular Function [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Impact of Insulin Resistance on Male Hormonal Health: Strategies for Optimal Testosterone Levels [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Optimizing Vitamin D for Androgen Balance in Hormone Replacement Therapy: Clinical Considerations [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Optimizing Men's Health: Understanding Allostatic Load and Hormonal Balance for Personalized Therapies [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Multimodal Endocrine Evaluation for Fatigue in American Men: Beyond Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Exploring Neurosteroid Modulation: A Breakthrough in Managing Stress-Related Endocrine Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators in Male Endocrine Health [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Role of Oxytocin in Male Endocrinology: From Physiology to Therapeutic Potential [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Precision Medicine in HRT: Genomic and Metabolomic Advances for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Role in Men's Steroid Hormone Metabolism: Emerging Insights and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Thyroid-Testicular Axis: Impact on Male Health and Fertility [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- EDCs' Impact on Male Health: Hormone Therapy and Detoxification Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Adipokines: Key Regulators of Male Endocrine, Metabolic, and Cardiovascular Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Ghrelin System Modulation: A New Frontier in Weight Management for Hypogonadal Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Somatostatin Analogues: Expanding Roles in Male Endocrinology and Health Management [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Chronobiology's Role in Optimizing Male Hormone Testing and Therapy Timing [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Function and Male Hormonal Health: Age-Related Decline and Therapeutic Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Inflammaging and Endocrine Senescence: Optimizing Hormonal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Trace Elements' Role in Hormone Metabolism for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomics Revolutionizes Male Endocrine Diagnostics in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Pharmacogenomics Revolutionizes Hormone Replacement Therapy for Men: Tailoring Treatment to Genetic Profiles [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise and Hormonal Dynamics in Men: Implications for Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Male Climacteric Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Personalized Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Neuroendocrine Integration of Energy Balance and Reproduction in American Men: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Multimarker Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment for American Males on Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Free and Bioavailable Hormones: Key to Male Endocrinology for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Prostate Health Safely During Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Pituitary Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-Term Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- HRT and Telomere Length: Impacts on Aging and Longevity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Subclinical Endocrinopathies in Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Health Impacts [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Male Biological Clock: Endocrine Impacts on Fertility and Offspring Health in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Frailty in Aging American Men: Understanding and Multimodal Intervention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- NAFLD and Male Endocrine Health: A Bidirectional Impact and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Opioid-Induced Endocrinopathy in American Men: Mechanisms, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Diurnal Hormone Variations: Impact on Men's Endocrinology and Therapy Optimization [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Reserve Testing in Men: Applications, Limitations, and Future Directions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- BMD Monitoring Protocols for Men on Hormone Replacement Therapy: Endocrinological Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- OSA's Endocrine Effects in Men: Beyond Testosterone to HPA, Thyroid, GH, RAAS [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormone Optimization: Preventing Sarcopenia in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Longitudinal Epigenetic Changes from HRT in American Men: Endocrinological Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- SHBG: Beyond Transport - Its Role in Male Hormonal and Metabolic Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Polycythemia in Men on Testosterone Therapy: Evidence-Based Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Biomarkers in Male Endocrinology: Growth Factors and Cytokines in Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Immunomodulatory Effects on Autoimmune Diseases in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- HPT Axis Recovery After Exogenous Testosterone: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neuropeptide Y: Key Regulator in Male Endocrine and Metabolic Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy Enhances Cognitive Function in Aging Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Luteinizing Hormone: Key Roles in Men's Health and Endocrinology [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Leptin Resistance in American Men: Endocrine Impacts and Targeted Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- ECS Influence on Male Reproductive Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Innovative Androgen Receptor Techniques Revolutionize Men's Hormone Therapy in the US [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- INSL3: A Stable Biomarker for Assessing Leydig Cell Function in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Post-Traumatic Hypopituitarism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Vasopressin's Role in Male Endocrinology: Therapeutic Potential and Clinical Applications [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- AMH's Expanding Role in Adult Male Endocrinology: From Fertility to Cardiovascular Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Inhibin B: Key Biomarker for Male Fertility and Testicular Health Assessment [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Long-term Endocrine Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury in Men: Management and Follow-up [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Chemotherapy-Induced Endocrine Disruption in Men: Monitoring and Intervention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hyperparathyroidism's Impact on Male Reproductive Health: Diagnosis and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Radiation-Induced Hypopituitarism in Men: Hormonal Deficiencies and Replacement Therapies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Impacts and Management of Male Endocrine Function [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hemochromatosis in Men: Endocrine Effects, Screening, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Cushing's Syndrome in Men: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Hormone Therapy Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Endocrine Insights into Male Sexual Desire Disorders: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Adrenal Incidentalomas in Men: Endocrine Evaluation and Management Algorithm [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hormonal Factors and Treatment Strategies for Male Stress Urinary Incontinence [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Optimizing GH and IGF-1 in Male Athletes: Performance, Health, and Ethics [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Osteoporosis in Men: Diagnosis, Endocrine Evaluation, and Multifaceted Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Enhancing Endocrine Resilience in American Men: Biological Mediators and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine Management of Hormone Therapy in Transgender Men: Protocols and Health Outcomes [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Male Hormonal Contraception: Endocrine Mechanisms and Clinical Progress in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- HRT in Male Fertility: Current Practices and Future Innovations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- AI Revolutionizes Precision Endocrinology for Personalized Men's Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Androgen Action: Molecular Biology and Targeted Endocrine Therapies in Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Validating and Implementing PROMs in Male Endocrinology for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- CGM's Role in Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men: Beyond Diabetes [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Integrative Endocrinology: Holistic Hormone Management for Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Wearable Tech Revolutionizes Hormone Monitoring for Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Telehealth in Male Endocrinology: Enhancing HRT Access and Effectiveness [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]

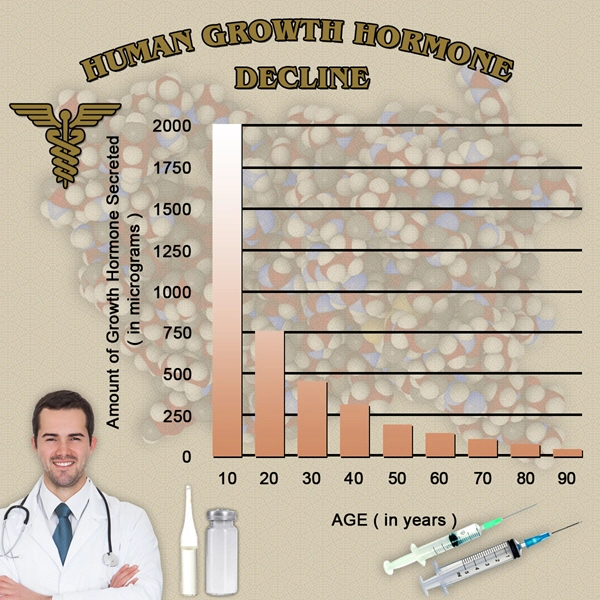
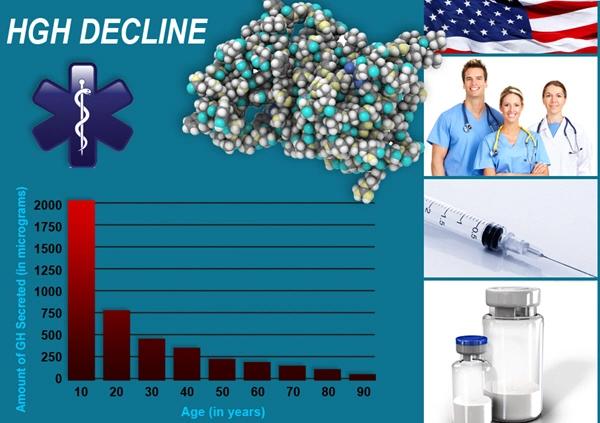
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 614