Introduction to Late-Onset Hypogonadism
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), also known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome associated with advancing age in men. It is characterized by a deficiency in testosterone levels, which can lead to a variety of symptoms affecting overall health and well-being. In the United States, where the male population is increasingly aware of health issues related to aging, understanding the influence of LOH on mood and energy is crucial.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of LOH
The symptoms of LOH can be subtle and often overlap with those of normal aging, making diagnosis challenging. Common signs include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, loss of muscle mass, and mood disturbances such as depression and irritability. To diagnose LOH, healthcare providers typically measure serum testosterone levels and assess the presence of clinical symptoms. It is essential for American men to consult with healthcare professionals if they experience these symptoms, as early detection and management can significantly improve quality of life.
The Link Between LOH and Mood
Research has established a strong connection between low testosterone levels and mood disorders. Testosterone plays a critical role in regulating neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for maintaining emotional stability. Studies have shown that men with LOH are at a higher risk of developing depression and anxiety. In the context of American men, who often face high levels of stress due to work and societal expectations, the impact of LOH on mood can be particularly detrimental.
Impact of LOH on Energy Levels
Energy levels are another critical aspect affected by LOH. Testosterone is vital for maintaining muscle mass and strength, which directly influence physical endurance and vitality. Men with LOH often report chronic fatigue and a noticeable decline in their ability to engage in physical activities. This can have a cascading effect on their overall health, as reduced physical activity can lead to weight gain, cardiovascular issues, and further exacerbation of mood disorders. For American men, who value an active lifestyle, the energy depletion caused by LOH can be particularly frustrating and impact their daily lives significantly.
Management and Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are effective treatments available for managing LOH. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the most common approach and has been shown to improve symptoms such as mood, energy levels, and sexual function. However, TRT is not suitable for everyone and should be administered under the supervision of a healthcare provider. Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can also play a significant role in mitigating the effects of LOH. American men are encouraged to adopt a holistic approach to managing their health, combining medical interventions with lifestyle changes for optimal results.
The Importance of Awareness and Early Intervention
Awareness about LOH and its impact on mood and energy is essential for American men. Early intervention can prevent the progression of symptoms and improve overall well-being. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating patients about the signs of LOH and the importance of seeking timely medical advice. By fostering a proactive approach to health, American men can better manage the challenges posed by LOH and maintain a higher quality of life as they age.
Conclusion
Late-onset hypogonadism is a significant health concern for American men, particularly in terms of its effects on mood and energy levels. Understanding the symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and exploring appropriate treatment options are vital steps in managing LOH effectively. By addressing this condition proactively, American men can enhance their emotional and physical well-being, ensuring a more fulfilling and active life in their later years.

- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Middle-Aged and Older Men [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on U.S. Men's Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Muscle Mass and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Exploring Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Current Treatments and Future Innovations [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impacts, and Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Lifestyle, and Medical Interventions for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Managing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Risks and Benefits of Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Early Detection and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits of Early Intervention in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cognitive Function and Therapeutic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Strategies for Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Societal Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Emotional Journey of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Coping and Support [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Health and Importance of Early Intervention [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Enhancing Patient Education and Screening in the US [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Risks, and Management Strategies for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Stigma, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, HRT Benefits, and Safety in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Multidisciplinary Care [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Stress and Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Males' Hormonal Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Careers and Workplace Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Males and the Vital Role of Family Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on American Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Financial Impact of Late-Onset Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Innovative Technologies Revolutionizing Late-Onset Hypogonadism Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevalence, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Mental Health Professionals' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Community Support and Management Strategies for Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis Journey and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Vital Role of Peer Support for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions in the US [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress Reduction Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Patient Advocacy's Crucial Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Detection, and Holistic Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Non-Pharmacological Approach to Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]

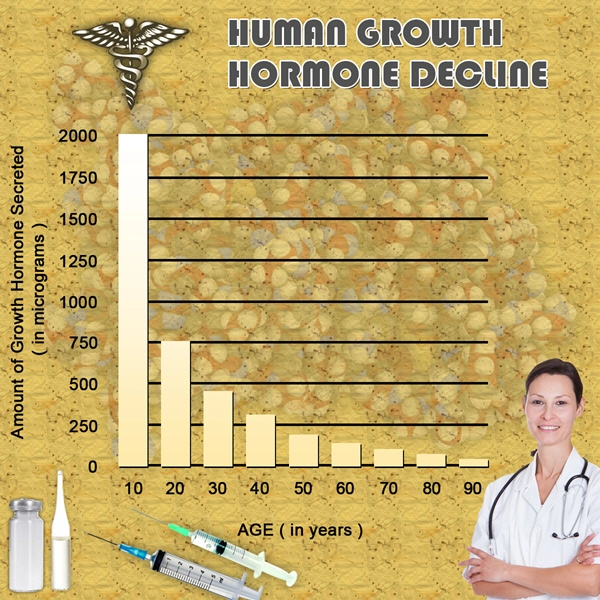
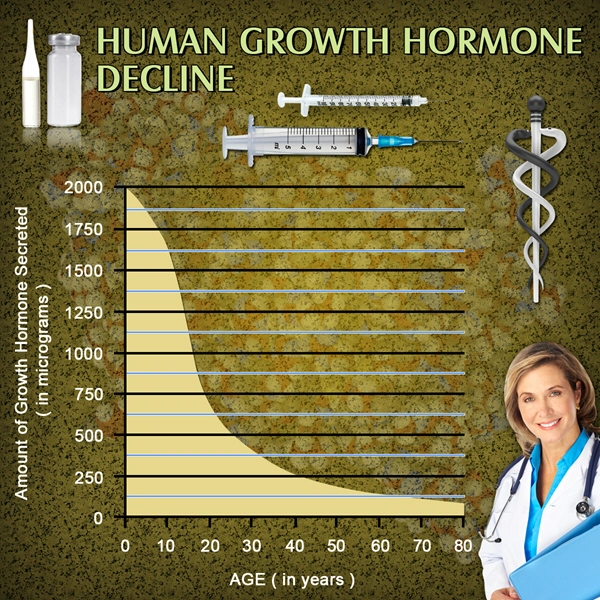
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 596