Introduction
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a persistent incapability to attain or maintain an erection suitable for sexual intercourse. Not a disease, it is rather a symptom of physical or psychological conditions. Unraveling the intricacies of impotence goes beyond the domain of urological study alone; it requires dappling into the depths of psychological realms. The psychological impacts attributed to impotence can be severe, inducing a range of emotions from embarrassment and frustration to severe anxiety and depression.
The Direct Connection
Physical and psychological factors are often intertwined in matters of impotence. A physical condition causing impotence, like obesity or diabetes, can lead to a psychological response like stress or anxiety. This anxiety can, in turn, exacerbate the ED.
Sexuality and Self-Image
Impotence can easily bruise the ego of any man. The societal constructs often falsely correlate virility to masculinity, hence impotence may shatter an individual's self-image. Patients suffering from ED may develop a sense of insufficiency and suffer from low self-esteem. The paradigm of sexuality in relation to identity and self-image makes impotence a much more emotionally fuelled condition than simply being a physical problem.
Social Stigma and Solitude
Impotence can lead to severe emotional backlash due to the social stigma attached to it. The reluctance to discuss sexual health issues can alienate someone suffering from impotence. The feeling of loneliness and isolation could heighten, leading to further psychological distress and making communication about the condition even more challenging.
Partnership and Relationships
The psychological turmoil is no less for partners of those suffering from impotence. It could give rise to misunderstandings, feelings of rejection, or lower self-esteem in partners. Therefore, it is essential that transparency and emotional support are encouraged in relationships dealing with impotence.
Mental Health Connection
Clinical studies have proven a strong association between impotence and mental health. Serious mental health conditions like depression and anxiety have the potential to cause or worsen impotence. Additionally, the stress and anxiety stemming from impotence could potentially lead to the development of mental health disorders.
Conclusion
While medical interventions and lifestyle changes may be required in the treatment of impotence, the psychological aspects associated can't be ignored. Counseling, therapy sessions, and couple counseling can be instrumental in dealing with the psychological impact. The acceptance and understanding of impotence need to be propelled, breaking past societal stereotypes, focusing on both physical and emotional wellbeing.

- Unveiling the New Frontiers in Treating Male Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: December 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Unspoken: Unmasking the Truth About Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Breaking Through the Shackles: A Voyage Through Male Impotence [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Facing the Invisible Battle: The Untold Challenges Surrounding Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Decoding The Enigma: Science Behind Impotence and Its Underlying Causes [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Reimagining Virility: The Journey Towards Understanding and Overcoming Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments Revolutionizing Impotence Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Erectile Dysfunction: Strategies to Combat Stigma and Improve Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Connection Between Erectile Dysfunction and Heart Health [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Testosterone's Role in Male Impotence and Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Stress and Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Navigating Impotence in Relationships: Essential Communication Strategies for Couples [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Confronting Impotence: Causes, Treatments, and Success Stories in American Men [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Psychological Impact of Impotence on Relationships: Navigating Communication and Intimacy Challenges [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Spectrum of Alternative Therapies for Managing Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Mastering the Challenge: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Treating Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Male Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Overcoming Impotence Through Lifestyle Changes [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Pathway: Counseling as a Cornerstone for Overcoming Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Impotence Unveiled: Men's Personal Triumphs Over Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: Causes, Diagnosis, Treatments, and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Emotional Navigation [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Impotence in Aging American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Medication-Induced Impotence: Causes, Management, and Empowerment Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Restorative Sleep: A Key to Enhancing Sexual Health and Combating Impotence in Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Economic, Emotional, and Relational Impacts Explored [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence Stigma: Encouraging Dialogue and Proactive Health Management [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Rebuilding Romance After Impotence: Redefining Intimacy and Strengthening Bonds [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Telemedicine Revolutionizes Impotence Care: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Diabetes and ED in American Men: Understanding Links, Risks, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Innovative Gadgets and Techniques Revolutionize Impotence Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Positivity and Mental Resilience: Key to Overcoming Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Obesity, Diet, and Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Strategies for American Men to Rekindle Passion and Intimacy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Enhancing Seduction and Intimacy Through Holistic Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Causes, Emerging Treatments, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Breaking Silence, Understanding Causes, and Exploring Treatments [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Psychological Approaches to Managing Impotence: CBT, Mindfulness, and Support [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Physical Therapy Enhances Sexual Performance, Addresses Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions of Impotence in America: Impact on Men's Health-Seeking Behaviors [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Counseling Strategies for Enhancing Self-Esteem in Men with Impotence [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Enhancing Erectile Function and Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Redefining Sexual Success: Beyond Impotence for American Men's Holistic Wellness [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring Impotence Treatments: From Injections to Implants and Emerging Therapies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Insurance Coverage for Erectile Dysfunction Treatments: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Anatomy of Impotence: Vascular, Neurological, and Hormonal Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Impotence: Partners' Role in Recovery and Relationship Strengthening [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Causes, Treatments, and Holistic Recovery Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Aphrodisiacs: Natural Remedies for Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Biochemical Insights into Impotence: NO, cGMP, Hormones, and Future Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Essential Vitamins and Minerals to Combat Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Work-Related Impotence: Understanding Stress Links and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Impotence: Insights for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impacting Male Sexual Health: Diet, Exercise, and More [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Impotence: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise as a Natural Remedy for Impotence: Enhancing Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: From Historical Remedies to Modern and Future Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Impotence: Unveiling Emotional and Financial Burdens on American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exploring Secondary Causes of Impotence When Medications Fail: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Navigating Emotional Challenges and Coping Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Navigating Identity, Intimacy, and Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Impotence in America: Masculinity, Stigma, and the Path to Healing [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Debunking Myths: Understanding and Treating Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: A Collaborative Approach to Sexual Wellness for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Smoking and Alcohol: Key Factors in Impotence Among American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Acupuncture as a Complementary Treatment for Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- American Men's Journey to Overcome Impotence: Resilience and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Impotence, Depression, and Anxiety: A Holistic Approach to Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Mindfulness and Meditation: A Holistic Approach to Treating Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Surgical Options for Impotence: Procedures, Recovery, and Risks [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Innovative Technologies Transforming Erectile Dysfunction Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Psychological Impacts and Relationship Dynamics Explored [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Impotence and Prostate Health: Causes, Connections, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Future of Impotence Treatment: Innovations and Hope for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Breaking the Silence on Impotence: Fostering Open Dialogue for Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Hacks to Manage and Overcome Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Male Impotence: Insights and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Key Nutrients and Foods to Combat Impotence and Boost Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Impotence and Chronic Illness: Understanding Links and Managing Challenges [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins Linked to Male Impotence: Urgent Need for Awareness and Prevention [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Innovative Drug Therapies and Gene Therapy Transform Impotence Treatment Landscape [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
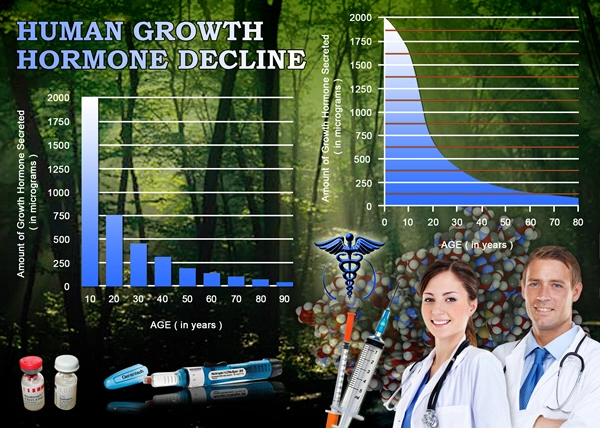


List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 395