Introduction
Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, is a significant health concern for many American males, particularly those in long-term care facilities. Effective medical monitoring is essential to manage this condition and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. This article explores the importance of vigilant monitoring of hypogonadism in long-term care settings and outlines strategies to enhance patient care.
Understanding Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism can manifest in various symptoms, including decreased libido, fatigue, depression, and loss of muscle mass. In older males, these symptoms can be exacerbated by other age-related health issues, making accurate diagnosis and management crucial. In long-term care facilities, where residents often have multiple comorbidities, the impact of hypogonadism can be particularly profound.
The Role of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of hypogonadism is vital for early detection and effective management. This involves routine blood tests to measure testosterone levels, as well as assessments of symptoms and overall health. In long-term care facilities, where residents are under continuous medical supervision, there is a unique opportunity to implement a structured monitoring program.
Strategies for Effective Monitoring
To ensure effective monitoring of hypogonadism, long-term care facilities should adopt a multi-faceted approach. This includes:
- **Routine Blood Testing**: Regular blood tests to assess testosterone levels are essential. These should be conducted at least annually, or more frequently if symptoms persist or worsen.
- **Symptom Assessment**: Healthcare providers should routinely evaluate symptoms associated with hypogonadism. This can be achieved through standardized questionnaires and regular consultations.
- **Comprehensive Health Reviews**: Given the potential impact of hypogonadism on overall health, comprehensive reviews should be conducted to assess any related health issues, such as cardiovascular disease or osteoporosis.
- **Patient Education**: Educating residents about hypogonadism and its symptoms can empower them to report changes in their health, facilitating early intervention.
Challenges in Long-Term Care Facilities
Monitoring hypogonadism in long-term care facilities can present several challenges. Staff shortages, limited resources, and the complexity of managing multiple health conditions in residents can impede effective monitoring. However, these challenges can be mitigated through strategic planning and resource allocation.
Implementing a Monitoring Program
To implement an effective monitoring program, long-term care facilities should:
- **Develop Protocols**: Establish clear protocols for monitoring hypogonadism, including frequency of testing and criteria for intervention.
- **Train Staff**: Ensure that healthcare staff are trained to recognize symptoms of hypogonadism and understand the importance of regular monitoring.
- **Utilize Technology**: Leverage technology, such as electronic health records and telemedicine, to streamline monitoring and improve communication between healthcare providers and residents.
- **Collaborate with Specialists**: Work closely with endocrinologists and other specialists to ensure comprehensive care for residents with hypogonadism.
Benefits of Effective Monitoring
Effective monitoring of hypogonadism can lead to numerous benefits for residents in long-term care facilities. These include improved quality of life, better management of symptoms, and reduced risk of complications associated with low testosterone levels. Additionally, early detection and treatment can help prevent the progression of related health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Monitoring hypogonadism in long-term care facilities is a critical component of comprehensive care for American males. By implementing structured monitoring programs, long-term care facilities can enhance the health and well-being of their residents. Through regular testing, symptom assessment, and collaboration with specialists, these facilities can ensure that residents receive the care they need to manage hypogonadism effectively. As the population ages, the importance of such monitoring will only increase, underscoring the need for proactive and vigilant healthcare practices.

- Hypogonadism and Sleep Disorders: A Bidirectional Link in American Males [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Effects of Hypogonadism on Muscle Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Hypogonadism and Impaired Wound Healing in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Nexus of Hypogonadism and Parathyroid Function: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Liver Function: Management and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Chronic Pain: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Treating Hypogonadism with Testosterone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Thyroid Dysfunction: Exploring Correlations and Clinical Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Prostate Health: Understanding Links, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Links to Cancer Risk and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Men's Health and Quality of Life: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Disorders: Interplay, Management, and Future Research in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Medical Imaging Advances in Diagnosing Hypogonadism: MRI, CT, and Ultrasound Techniques [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: TRT Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Health: Diagnosis, TRT, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism: A Collaborative Approach by Medical Specialists [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Medicines for Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Screening Protocols and Recommendations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Addressing Psychological Needs Through Tailored Counseling [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Treatment Options and Outcomes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Neurological Health in American Males: Cognitive and Mood Effects [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Hearing Loss: Exploring the Hormonal Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in American Males with Kidney Disease: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Treatment Advances: Trends, Therapies, and Lifestyle Interventions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Blood Pressure: Symptoms, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Cholesterol: Implications for Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: Mechanisms and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Medical Innovations Transform Hypogonadism Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Joint Health: Treatment and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Headaches: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medical Nutrition Therapy for Managing Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Technology Revolutionizes Hypogonadism Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Balance Disorders: Exploring the Link and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Anemia in American Males: Diagnosis, Management, and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Eye Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Medical Rehabilitation for Hypogonadism: Enhancing Quality of Life in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Preventing Hypogonadism in American Males: Strategies and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Emotional Impact: Understanding and Managing Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Allergies: Exploring Links and Implications for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Dental Health: A Comprehensive Overview for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and GERD: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Vision: Understanding Testosterone's Role and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Medical Social Workers: Vital Support for Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism-Related Fatigue: Therapies and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Urinary Health: Diagnosis, Management, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Link to Peripheral Neuropathy in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Research [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Strategies to Enhance Adherence in Hypogonadism Treatment Among American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Accelerated Skin Aging in American Men: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Sinus Health: Exploring Hormonal Links and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Innovative Medical Devices Revolutionize Hypogonadism Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Gallbladder Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in Postmenopausal Women: Symptoms, Treatment, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Management and Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Wound Healing in American Males: Testosterone's Crucial Role [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism Linked to Impaired Lymphatic Function in American Males: Study Insights [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Empowering Nurses in Hypogonadism Care: Education Strategies and Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Ear Health: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Managing Hypogonadism in Men with Chronic Illnesses: Strategies and Challenges [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Medical Counseling Enhances Hypogonadism Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Spleen Health: Insights and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Thymus Health in American Males: Symptoms, Management, and Research [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Endocrine Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Pituitary Health: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Nutrition Management of Hypogonadism: Role of Medical Dietitians [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Parathyroid Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Adrenal Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
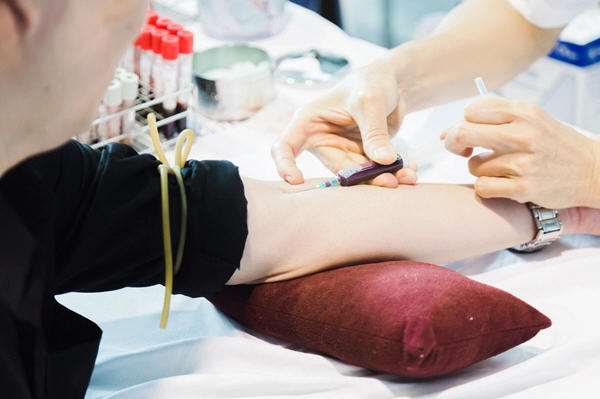
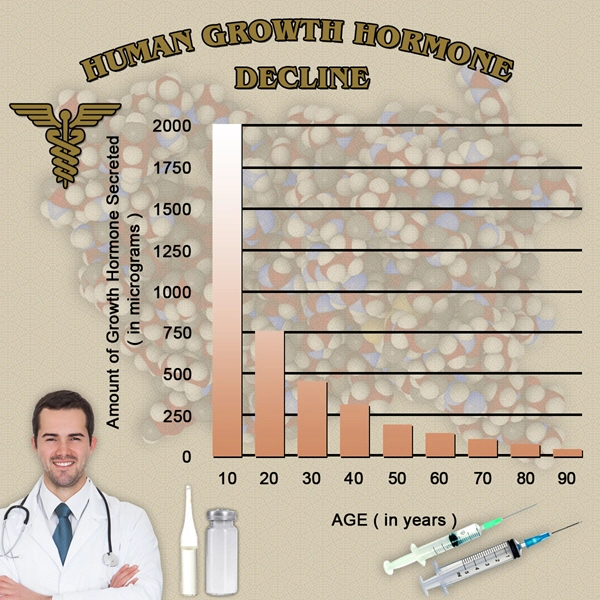
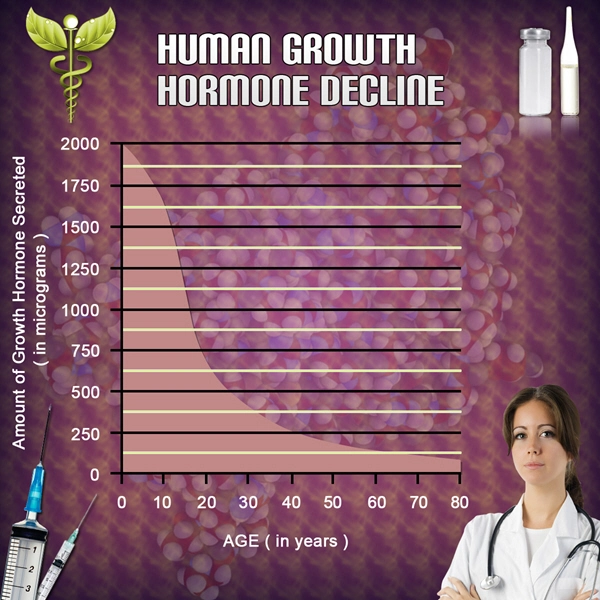
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 578