The Dash Diet is a balanced diet, designed to get an individual all of the nutrients that they need in a strict diet, with an emphasis on maintaining a reasonable and responsible salt intake.
The Dash Diet is similar to some other diets including the Mayo Clinic Diet, the Mediterranean Diet, the TLC Diet, and the Vegetarian Diet. Specifically, DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension.
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/253315139
Video Download: The Dash Diet Overview
Video Stream: The Dash Diet Overview
The ultimate goal of the DASH diet is to alleviate or prevent hypertension, also known as high blood pressure. Hypertension is a dangerous circulatory state which significantly increases risks associated with heart and cardiovascular health.
The DASH Diet was developed in cooperation with the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and its authors simultaneously claim that the diet can improve blood pressure while also making it easier to lose weight.
What is the Theory Behind the DASH Diet?
The DASH Diet recognizes that certain nutrients are vital to preserving healthy blood pressure, and builds a diet around responsibly providing the dieter with these nutrients. The four nutrients that are considered most important in promoting heart health are fiber, protein, calcium, and potassium.

Unlike many other diets that encourage the dieter to keep track of nutrition and calorie counts, this diet focuses primarily on moderation without excessive deliberation or calorie-counting.
These are the three aspects of the DASH Diet:
Eat Foods That Encourage Hypertension Sparingly -- The DASH Diet recommends limiting the intake of red meat, sweets, processed foods, and calorie-dense foods that provide little nutrition.
Eat Foods That Are Good For You and Your Heart – Foods such as lean meat, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and low-fat dairy are encouraged. It's important to note here that this is not a vegetarian diet.
Limit Salt Intake -- Salt intake is strongly correlated with hypertension. Salt exacerbates existing high blood pressure, and may also contribute to the formation of such issues when used in excess.
You don’t have to track each one, though. Just ensure that the foods highlighted above are eaten in abundance (veggies, whole grains, fruits, low-fat dairy, and lean protein) while shunning those that we’ve unfortunately grown to love (calorie- and fat-laden sweets and red meat). Top it all off by cutting back on salt, and voilà!
The DASH Diet is an extensively researched diet plan, and there are two primary guides designed to show you how it's done. Both are produced by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. One is short and to the point, and the other is more elaborate and gets into the science and specifics of the diet.
First, the DASH Diet takes into account your activity level as well as your age to provide you with a rough gauge of how many calories you need to consume daily. Second, the guide for the diet contains an extensive list of foods that meet your nutritional needs most effectively. Third, the menu simply encourages you to limit sodium consumption.
 The DASH Diet is not a complicated diet, which likely will attract many dieters looking for a no-nonsense diet plan.
The DASH Diet is not a complicated diet, which likely will attract many dieters looking for a no-nonsense diet plan.
On the other hand, other dieters that are looking for more direct meal-to-meal guidance may prefer a different diet plan, even if it is close to the current one described.
How Can I Lose Weight with the DASH Diet?
To lose weight with the DASH Diet, merely take the caloric recommendations for your age and drop them down by 300-500 calories per day. This builds a caloric deficit into your nutritional recommendations, which will help you lose weight while simultaneously meeting your body's dietary needs.
Of course, to maximize the weight-loss benefits of this diet, you'll benefit significantly from increasing your activity level with a combination of anaerobic and aerobic activity.
Does the DASH Diet Improve Cardiovascular Health?
There is compelling evidence that the DASH Diet succeeds significantly in reducing the severity of hypertension, and that it can also prevent high blood pressure in at-risk patients. Hypertension is associated with a wide variety of dangerous cardiovascular conditions, including stroke, heart failure, and heart disease.
By following this diet protocol, you can expect to improve your blood pressure while also promoting healthier cholesterol balance, with a reduction in LDL cholesterol associated with poor health outcomes and an increase in HDL cholesterol, which is associated with improved heart health.
with poor health outcomes and an increase in HDL cholesterol, which is associated with improved heart health.
Also, the DASH Diet reduces triglycerides in the bloodstream, which are strongly associated with heart disease.
The ultimate goal of the creators of the DASH Diet was to quantify what is generally accepted in the medical community to be a diet healthy for the heart, which is a diet low in salt, sugar, and saturated fat and which is high in vegetables and nutrient-dense fruits.
Can the DASH Diet Reduce the Risk of Diabetes?
There is resounding evidence that the DASH Diet is fantastic for patients that are at risk for diabetes. The specifics of the DASH Diet share a lot in common with recommendations offered by the American Diabetes Association.
That means that this diet is simultaneously suitable for patients that want to avoid hypertension as well as diabetes, and when pursued in combination with dietary restriction and increased activity level, the diet can also produce significant weight loss benefits.
Are There Any Risks Associated with the DASH Diet?
There are no health issues associated with following this diet, although there is a chance that patients who suffer a few specific health conditions may need to alter the menu to meet their needs or protect their health. Before starting even the safest diet, discuss it with your doctor if you have any health issues which have any potential to conflict with your regimen.
How Does the DASH Diet Relate to Currently Agreed Upon Dietary Recommendations?
Salt -- The DASH Diet recommends salt consumption less than 2,300 milligrams per day, although patients that have kidney disease, diabetes, or hypertension are advised to consume no more than 1,500 milligrams per day, as well as all African Americans and men and women over the age of 50.
Fat -- The DASH Diet is designed to significantly reduce the amount of saturated fat you eat while keeping you in the 20-35% fat intake range that is ideal.
Protein -- This diet focuses on lean meat, and provides plenty of protein to meet your daily needs.
 Carbohydrates -- It's essential to control both the number of carbohydrates that you eat daily as well as their source. The DASH Diet strictly limits sweets and simple carbs, encouraging dieters to get their carbohydrates from more complex sources.
Carbohydrates -- It's essential to control both the number of carbohydrates that you eat daily as well as their source. The DASH Diet strictly limits sweets and simple carbs, encouraging dieters to get their carbohydrates from more complex sources.
Vitamin B12 -- The DASH Diet more than meets the minimum standards for this nutrient. Vitamin B12 is found in high concentrations in eggs!
Calcium -- As the DASH Diet places a premium on cardiovascular health, it makes sense that the diet provides more than enough calcium to meet your daily needs.
Potassium -- The DASH Diet is one of the only diets which successfully meet nutrition recommendations about potassium. Ideally, you should be getting 4,900 milligrams of potassium per day.
Fiber -- Fiber is central to the success of the DASH diet, because the food places a premium on satiety, and fiber is one of the best things that you can eat to feel full. Fiber also encourages healthy digestion.
Vitamin D -- The DASH Diet includes no recommendations for Vitamin D, but it's important to get at least 15 micrograms daily, whether through diet, sunlight, supplementation or a combination of the three.
Reference

- Our Most Popular Diet Injection Programs (Call for Inquiry) [Last Updated On: December 28th, 2024] [Originally Added On: September 8th, 2020]
- How to Use Fasting to Boost Human Growth Hormone Levels [Last Updated On: January 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 12th, 2021]
- Magnesium Supplementation for a Healthier You [Last Updated On: January 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 25th, 2021]
- The Benefits of Intermittent Fasting: Lose Weight, Boost HGH, and Improve Glucose Levels [Last Updated On: January 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 8th, 2021]
- Confused About Intermittent Fasting? [Last Updated On: November 15th, 2024] [Originally Added On: February 19th, 2021]
- The Do's and Don'ts of Calcium Supplements – Can I Grow Taller? [Last Updated On: November 22nd, 2024] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2021]
- Benefits of Adding More Citrus Fruits to Your Diet [Last Updated On: November 8th, 2024] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2021]
- The Benefits of Vitamin B12 -- Boost Metabolism and Energy with Vitamin B12 [Last Updated On: February 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: May 11th, 2021]
- Romaine Lettuce: Guinea Pigs Like It -- Why Not You? [Last Updated On: November 9th, 2024] [Originally Added On: June 12th, 2021]
- How to Lose Weight on a Plant-Based Diet and Keep the Weight OFF! [Last Updated On: November 16th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 6th, 2021]
- Frozen Foods are Underrated: The Healthiest and Most Affordable Frozen Foods [Last Updated On: November 10th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 18th, 2021]
- The “Soyboy” Idea – Do Soy-based Foods Feminize Males? [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 28th, 2021]
- Avoid These Foods That Reduce Testosterone [Last Updated On: October 12th, 2024] [Originally Added On: June 28th, 2022]
- Six Vitamins to Focus On if You Want Thicker, Youthful-Looking Hair [Last Updated On: February 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 22nd, 2022]
- What You Need To Know About Intermittent Fasting [Last Updated On: October 29th, 2024] [Originally Added On: December 22nd, 2022]
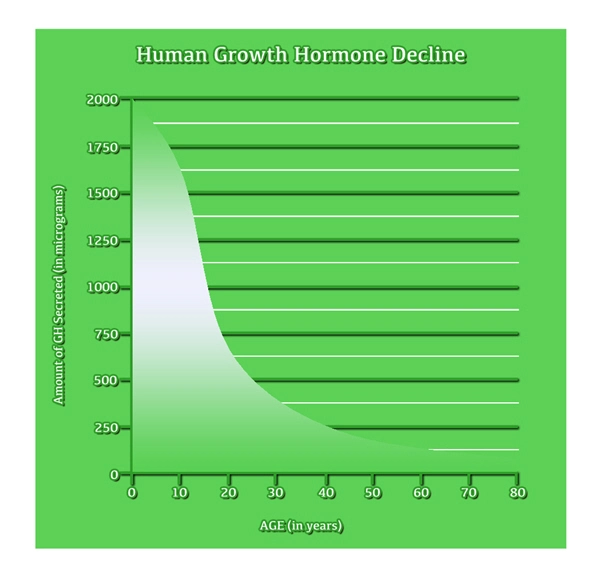
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 1284