Introduction to Body Building
Body building, a discipline that combines rigorous exercise with a strategic dietary approach, has gained significant popularity among American males. While the pursuit of a sculpted physique is commendable, it is crucial to navigate through the myriad of myths and embrace the medical facts that underpin this endeavor.
Myth: Body Building is Only About Lifting Weights
Contrary to popular belief, body building is not solely about lifting weights. It is a holistic approach that integrates strength training, cardiovascular exercises, and a balanced diet. Medical science supports the inclusion of all these components for optimal health and muscle development. Strength training indeed plays a pivotal role in muscle hypertrophy, but cardiovascular exercises are essential for cardiovascular health and overall fitness. A diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats is vital to fuel workouts and aid in recovery.
Fact: Proper Nutrition is Key to Successful Body Building
Nutrition is the cornerstone of effective body building. American males often fall into the trap of consuming excessive protein, believing it to be the sole nutrient necessary for muscle growth. However, medical research indicates that a balanced intake of macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—is essential. Proteins are crucial for muscle repair and growth, but carbohydrates provide the necessary energy for intense workouts, and fats are vital for hormone production, including testosterone, which is integral to muscle building.
Myth: Supplements are a Shortcut to Muscle Gain
The market is flooded with supplements promising rapid muscle gain, but the reality is far from these claims. While some supplements, like whey protein and creatine, can aid in muscle recovery and performance, they are not magic bullets. Over-reliance on supplements can lead to health issues, including kidney and liver strain. Medical professionals advocate for a diet-first approach, with supplements used only to fill specific nutritional gaps.
Fact: Rest and Recovery are Crucial
One of the most overlooked aspects of body building is the importance of rest and recovery. American males often push their bodies to the limit, believing that more workouts equate to better results. However, medical science underscores the necessity of adequate rest for muscle repair and growth. Overtraining can lead to injuries and hinder progress. Incorporating rest days and ensuring sufficient sleep are essential components of a successful body building regimen.
Myth: Body Building Leads to Inflexibility
There is a misconception that body building results in reduced flexibility. However, this is not inherently true. Incorporating stretching and mobility exercises into a body building routine can enhance flexibility and prevent injuries. Medical studies have shown that well-rounded fitness programs that include flexibility training can maintain or even improve range of motion.
Fact: Body Building Can Improve Mental Health
Beyond the physical benefits, body building has significant mental health advantages. Engaging in regular physical activity is known to reduce stress, alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, and boost self-esteem. For American males, who may face societal pressures to conform to certain body ideals, body building can be a constructive outlet for stress and a means to improve overall well-being.
Conclusion: Embracing a Balanced Approach
In conclusion, body building for American males is a journey that requires a balanced approach, grounded in medical facts rather than myths. By integrating strength training, cardiovascular exercises, proper nutrition, adequate rest, and mental health considerations, individuals can achieve their fitness goals in a healthy and sustainable manner. As with any fitness regimen, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and ensure safety and efficacy.

- Maximizing Longevity Through Bodybuilding: Insights from Geriatric Medicine for American Males [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Approaching Mental Wellness Through Physical Strength: Insights into Body Building as Therapeutic Intervention [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Enhancing Bodybuilding Performance and Injury Prevention: The Critical Role of Physical Therapy [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Essential Nutritional Strategies for Effective Bodybuilding [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring the Synergy Between Bodybuilding and Diabetes Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Bodybuilding: Effects on Muscle, Fat, and Bone Health [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Strength Training's Role in Enhancing Cardiovascular Health Among American Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Orthopedic Health Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders: Prevention, Nutrition, and Rehabilitation [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Dangers of Anabolic Steroid Use: Health Risks and Safe Practices for Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Optimizing Hormonal Dynamics in Bodybuilding: Key Strategies for Health and Performance [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring the Psychological Benefits of Bodybuilding for American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Strategy to Combat Obesity and Enhance Metabolic Health in Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- The Impact of Bodybuilding on Sleep: Patterns and Quality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Harnessing the Power of Bodybuilding to Alleviate Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Health Risks in Competitive Bodybuilding: Steroids, Organ Damage, and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Post-Surgery Rehabilitation Enhanced by Bodybuilding for American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Injury Prevention Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders: Techniques and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Addiction Recovery: Psychological and Physiological Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Strategic Approach to Managing Hypertension in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Endocrine System: Hormonal Fluctuations and Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Body Building as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoporosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immune Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Kidney Health: Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Lifestyle Diseases: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Body Building: A Powerful Antidote to Stress and Anxiety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Body Building in Pediatric American Males: Growth, Nutrition, and Psychological Impacts [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Lung Function: A Respiratory Therapist's Insight [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Debunking Menstrual Cycle Myths in Bodybuilding: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Potent Strategy Against Age-Related Muscle Loss in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Body Building Benefits and Risks for Sickle Cell Disease Patients [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Heart Health: Risks, Impacts, and Cardiologist's Guidance [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Managing COPD in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Gut Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Essential Vitamins and Supplements for American Male Bodybuilders: A Medical Review [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Muscle Growth for American Male Bodybuilders: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding for New Fathers: Enhancing Postnatal Recovery and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Prevention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Body Building as a Non-Pharmacological Strategy for Parkinson's in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Metabolic Impact: Muscle Growth, Insulin Sensitivity, and Health Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Comprehensive Anti-Aging Strategy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Orthostatic Hypotension in American Male Bodybuilders: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Asthma and Bodybuilding: Safe Integration and Health Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Body Building's Potential to Reduce Dementia Risk in American Males Explored [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Approach for Mood Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Techniques to Prevent Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Strategy for Managing PTSD in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Psychological Impact on American Teenage Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: Empowering American Males Against Chronic Degenerative Diseases [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Mental Resilience in American Men: A Comprehensive Insight [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Male Menopause and Body Building: Navigating Fitness in Andropause [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Liquid Diets for Bodybuilders: Efficacy, Risks, and Medical Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Managing Arthritis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Preventing and Managing Common Bodybuilding Injuries in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hydration's Critical Role in Bodybuilding: Guidelines and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Body Building Reduces Colon Cancer Risk in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immune Health: A Vital Component for American Men's Wellness [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Cognitive Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Recovery Tool for American Men Post-Chemotherapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Body Building and Heart Health: Risks, Benefits, and Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Therapeutic Approach for American Men with Rheumatoid Arthritis [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Essential Safety Precautions for American Male Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Medically Supervised Bodybuilding: Safe Weight Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Metabolism: Muscle Mass, Hormones, and Health Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Bone Density in American Males: Strategies and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Cardiovascular Fitness: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Life Expectancy: Benefits, Risks, and Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Hormonal Health in American Males: Balancing Key Hormones [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Flexibility Training: Essential for Enhancing Bodybuilding Performance and Health [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Stretching: Enhancing Performance and Preventing Injuries in Bodybuilding for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Gut Health: Maximizing Muscle Growth Through Digestive Wellness [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Stress Management for American Males: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Recovery for American Males Post-Joint Replacement Surgery [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Complementary Approach to Managing Sciatica in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Vegetarian Bodybuilding: Strategies for Muscle Growth on a Plant-Based Diet [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Structured Bodybuilding: Preventing Low Back Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Chiropractic Care: Preventing and Managing Back Pain in Bodybuilding [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Therapeutic Approach for Men with ADHD [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
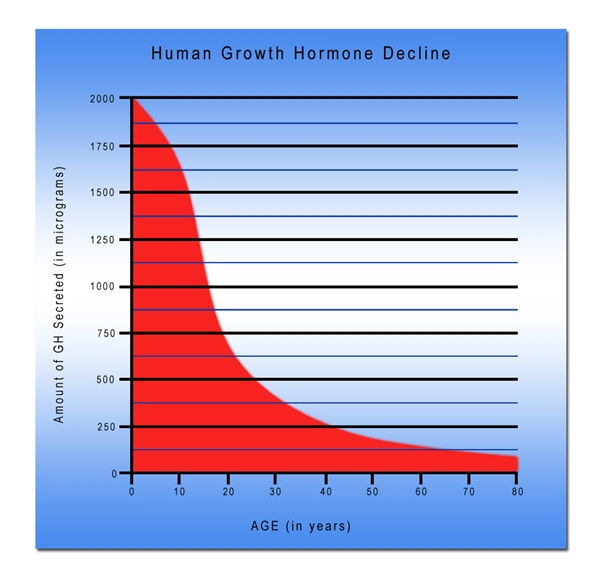
List of USA state clinics - click a flag below for blood testing clinics.
Word Count: 577